background
Because the bolt is subjected to axial stress for a long time, the propagation direction of the thread fatigue crack is generally perpendicular to the bolt axis.
Through the comparison of experiments, this paper gives a more practical magnetic particle detection technology, which solves the technical problem of fatigue crack detection at the thread root.
High-strength bolts are widely used in the petrochemical industry. They have the characteristics of high strength, high stress and long-term service. In order to ensure safe use, bolts are often tested.
Domestic bolt testing mainly uses ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing and penetrant testing.
The electric power industry introduced technical guidelines for ultrasonic testing of high-temperature fastening bolts in 2000, but it is difficult to promote it because of the low detection rate of fatigue cracks at the thread roots.
For high-strength bolts, the most fatigue-prone parts are the thread roots of the first, second, and third turns near the middle of the stud. There is no mature detection method for these parts.

1、Fatigue crack generation mechanism
If one or more points on the material produce stress and strain, after a sufficient number of changes, cracks or complete fracture will eventually occur, and the structure will gradually change. The American Society for Testing and Materials refers to this irreversible process as fatigue .
It can be seen that the root cause of fatigue is stress concentration.
Stress concentration is a phenomenon in which the local stress of a solid increases significantly. It generally occurs in holes, angles, gaps, grooves, and parts with rigidity constraints, which can cause cracks and even break brittle materials.
There are threads on the screws of high-strength bolts, which is equivalent to forming a gap. The stress is at the root of the thread. The stress concentration is formed due to the sudden change of the cross-section. For the high-strength bolts of the container, it is also subject to the rigidity of the shell and pressure changes as well as a long time. Service has aggravated the stress concentration phenomenon and is prone to fatigue.
For high-pressure and ultra-high pressure equipment in the petrochemical industry, the most fatigue-prone part is the thread roots of the first, second, and third turns near the middle of the bolt. Due to long-term axial stress, the propagation direction of fatigue cracks is generally perpendicular to the bolt axis.
2、Selection of detection methods
The fatigue cracks of high-strength bolts are in the form of fine-grained porcelain and are located at the root of the thread. Due to the subtle flaws and special locations, it is difficult to detect.
Maoming Weite Testing Technology Co., Ltd. has carried out one-by-one test on the manual ultrasonic, phased array and fluorescence penetration testing methods introduced in the relevant literature, but the testing results are not satisfactory.
Because of the special structure, for the ultrasonic detection method, the position of the reflected wave of the defect and the reflected wave of the thread is too close, and the clutter is so large that it cannot be distinguished; for the penetration inspection, the cleaning work after penetration is difficult to grasp, and the cleaning is insufficient. If there is too much cleaning, defects cannot be detected.
After repeated experiments, it was decided to adopt the fluorescent magnetic powder detection method, and a special process was explored, and the detection effect was relatively ideal.
3、Fluorescent magnetic powder detection method
3.1 Wet fluorescent magnetic particle detection
Use water as a carrier to make a magnetic suspension with a concentration of 0.7~0.8g/L and use the pouring method.
3.2 Continuous method
The magnetization time is 1~3s. The application of the magnetic suspension and the observation of the magnetic trace display are completed within the magnetization energization time, and the magnetization can be stopped after stopping the application of the magnetic suspension for at least 1s.
3.3 Winding cable method
A magnetic field parallel to the axis of the bolt is generated, and the fatigue crack at the root of the thread cuts the magnetic field lines.
Taking the φ76×630 bolt as an example, the number of turns of the coil is N=5, and the calculation formula of the magnetizing current (I) is shown in formula (1). The current can fluctuate by ±10%.

(1)
3.4 Sensitivity test piece chooses C8/50 type small test piece
In order to verify the sensitivity of the system, a ring belt with a width of 10mm and a depth of 3mm was machined at a distance of 5mm from the middle of the bolt to the first circle of threads to verify the magnetization effect of the root of the thread. See Figure 1 for details.
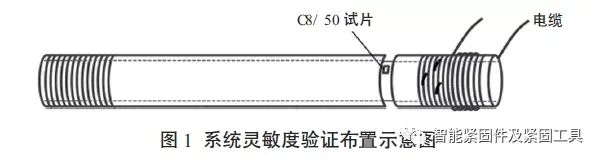
(图1)
3.5 Artificial defect production
As shown in Figure 1, at the thread roots of the first, second, and third turns, a 0.1mm molybdenum wire is used to cut artificial defects with a depth of 0.5mm, 1.0mm, and 1.5mm, respectively, with a length of 8mm.
3.6 Segment detection
Since the threads and the machining marks on the threads also cut the magnetic lines of force, it is easy to form magnetic marks accumulation and make it impossible to detect.
After many experiments, it is found that the method of segmented detection is the most ideal.
The specific method is: draw an inscribed hexagon on the end face of the bolt (Figure 2), and ensure that the two sides of the inscribed hexagon are perpendicular to the ground, and the arc circle corresponding to the two sides is a detection area;
The magnetic suspension is poured from above the vertices of the inscribed hexagon. Each magnetization can detect two arcuate circumferential areas, and 3 magnetizations can detect a complete circumference.
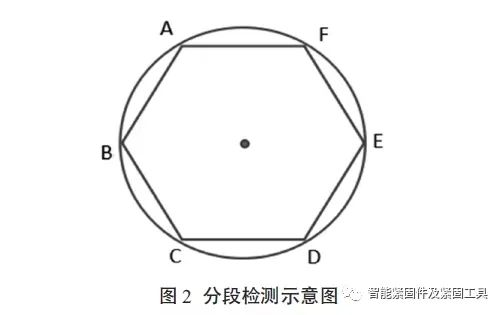
(图2)
As shown in Figure 2, A!B and D!E, B!C and E!F are once magnetized, and F!A and C!D are once magnetized.
When AB is perpendicular to DE and the ground, the non-correlated displays on A!B and D!E are greatly reduced.
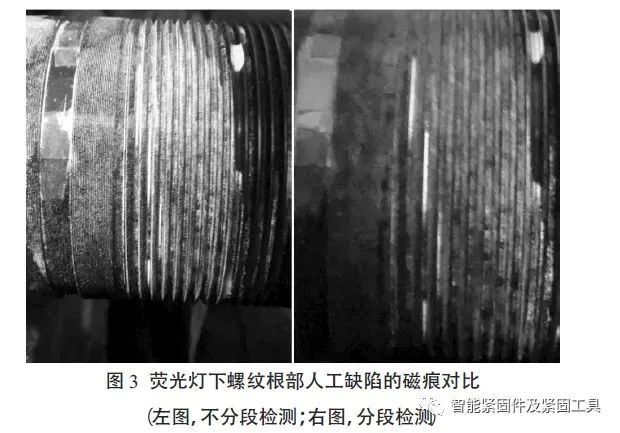
When observing under a fluorescent light, it was found that the accumulation of magnetic marks on A!B and C!D was significantly reduced, the artificial defects located at the root of the thread were eye-catching yellow-green, and the magnetic marks were displayed very clearly, and they could be observed without using a magnifying glass.
See Figure 3 for details.

(图3)
It can be seen that the method of segmented detection can well solve the problem of magnetic powder accumulation and can ensure the effective detection of fatigue cracks at the thread root.
It can be seen from the segmented inspection diagram in Figure 3 that the magnetic traces of the three artificial defects set are very obvious, and they can all be detected effectively, with a detection rate of 100%.
3.7 demagnetization
Because high-strength bolts are magnetic, they will adsorb ferromagnetic particles, which may cause rust or corrosion.
Therefore, after the magnetic particle inspection is over, it must be demagnetized.
As long as the current in the cable wound on the bolt is gradually reduced to zero.
3.8 Dedicated process
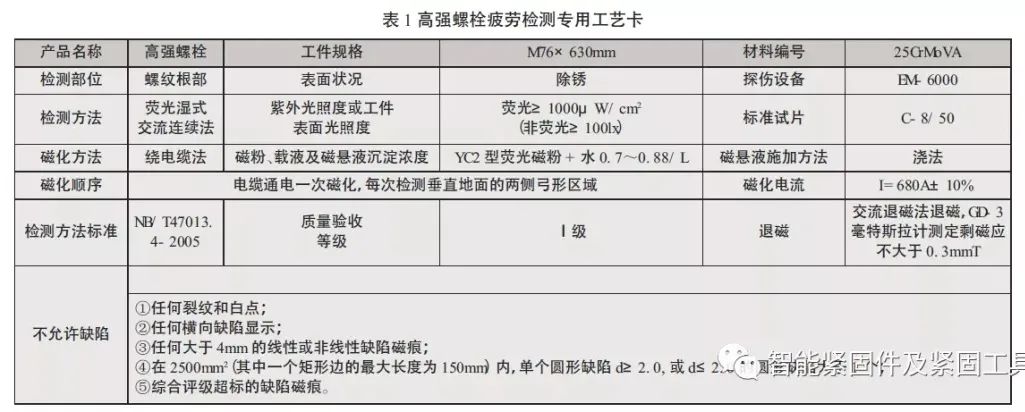
In order to facilitate the work and better guide the practice, a special craft card (Table 1) is specially made.
4、Concluding remarks
The thread of the diesel hydrogenation reactor bolt is detected by the fluorescent magnetic powder detection method. The result is that the detection effect is very good according to the given special process. The relevant display and the non-relevant display can be clearly distinguished, and the defect can be effectively detected. .
When testing, pay special attention to that the chord of the bow-shaped testing surface should be as perpendicular to the ground as possible, and the concentration of the magnetic suspension should be appropriate to ensure that no magnetic powder accumulation is formed on the testing surface to ensure the quality of the test.
Through the detection, it is possible to avoid the work of high-strength bolts from being damaged, and to provide guarantee for the safe operation of petrochemical plants.